1 - PRINCIPLES OF CHEMISTRY
Ionic bonding -
- Atoms lose or gain electrons to form charged particles (ions)
- Strongly attracted to one another because of the opposite charges - electrostatic attrcation
- High melting and boiling points
- Dot and cross diagrams (with square brackets and charge)
Gaining electrons = reduction
Shell less than half full of electrons -
- Left hand side of periodic table
- Want to become more stable like the noble gases
- Try to lose the electron - easier than completing shell
- Become positive
- Gives electron to oppositely charges atom wanting to complete shell - stick together
- Right hand side of periodic table (group 6 and 7)
- Gain extra electrons to complete shell
- Become negative
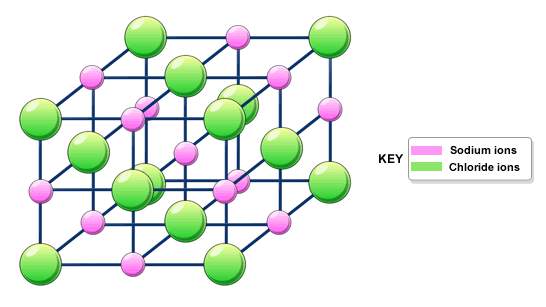
Giant ionic structures -
- Compounds with ionic bonding always have giant ionic structures
- Ions held together in closely packed 3D lattice (attraction between oppositely charged ions - very strpmg)
- A lot of energy is needed to overcome the strong forces of attraction - high melting and boiling points
- The more charged it is, the stronger the forces of attractions are

No comments:
Post a Comment